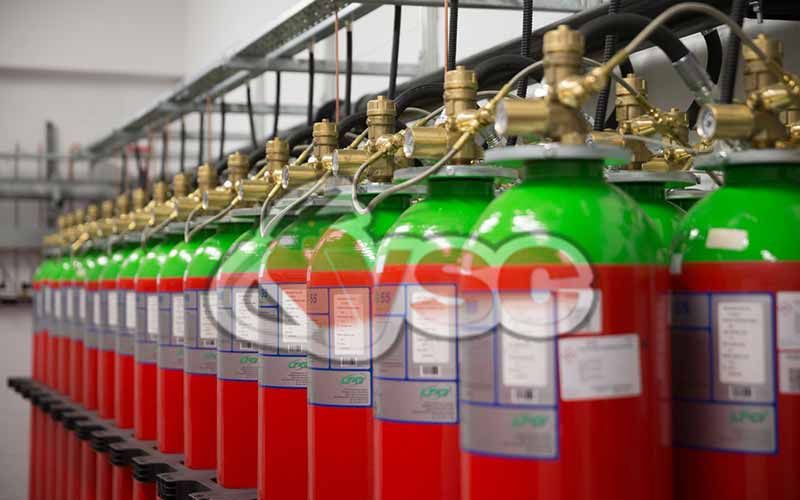
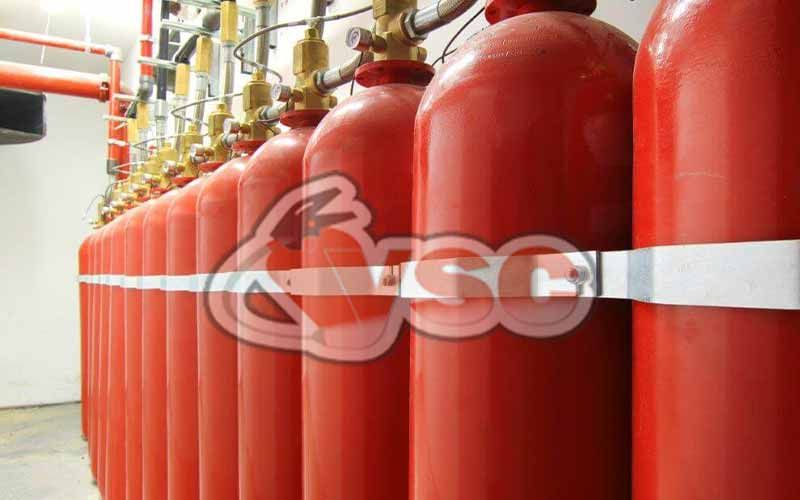
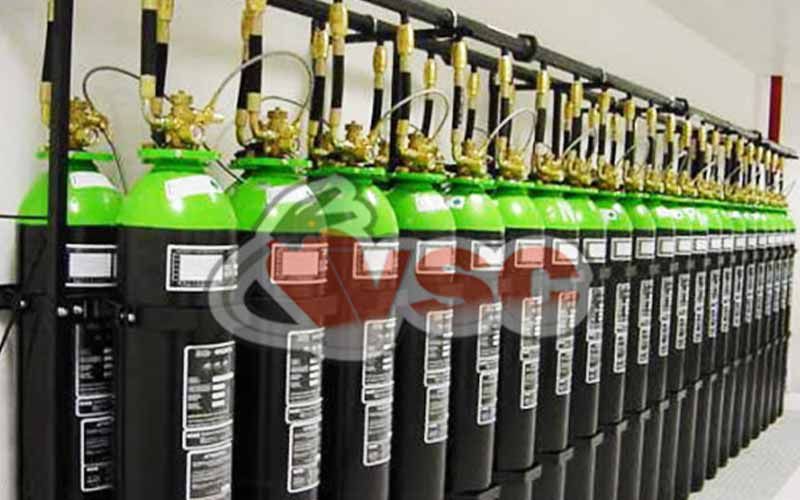
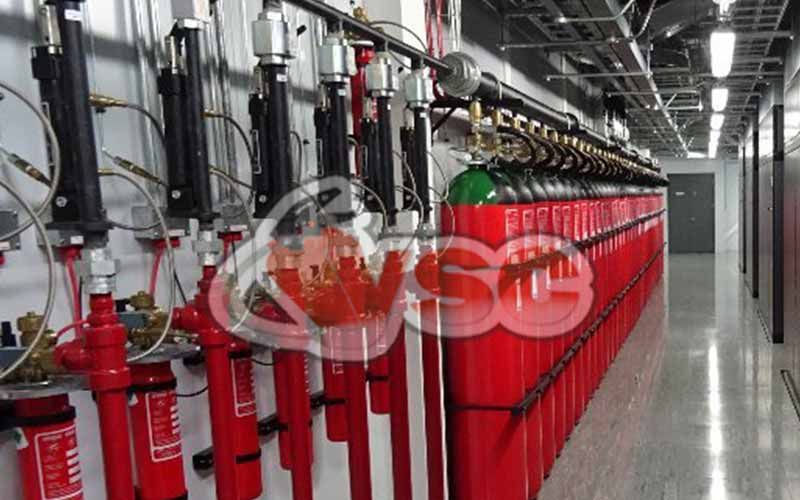
Argon Gas Extinguishing Systems (INERT Gas, Turnkey)
Fires are among the disasters that occur in our world today and can cause significant damage to property and pose serious risks to human life. Therefore, it is crucial to take all necessary precautions to prevent and combat fires effectively. Various fire suppression systems can be employed for this purpose, and one of the most commonly used and advantageous systems is the argon gas fire suppression system.
Argon gas fire suppression systems stand out with their distinct features and are widely adopted by people to mitigate potential disasters. By using such systems, the aim is to prevent major catastrophes and protect lives and property from the powerful effects of fires.
Argon Gas Fire Suppression Systems
Argon gas fire suppression systems possess various characteristics, including:
- Naturally occurring inert gas in the atmosphere.
- Colorless, odorless, and non-conductive.
- ODP=0 (Does not harm the ozone layer/Environmentally friendly).
- GWP=0 (No impact on global warming).
- Suppresses fires by reducing the oxygen concentration in the environment.
- Leaves no residue and requires no cleanup after discharge.
- Safe for use in occupied spaces.
- Designed for Class A fires with a design concentration of 41.9% (NOAEL 43%, LOAEL 52%).
- Used as a replacement for Halon 1301 systems.
- Cylinder pressure of 200 or 300 bars, and piping pressure of 55-60 bars.
- Complies with standards such as ISO 1450, UNE 23570, and NFPA 2001: IG01.
- Chemical Formula: Ar (minimum purity of 99.99%).
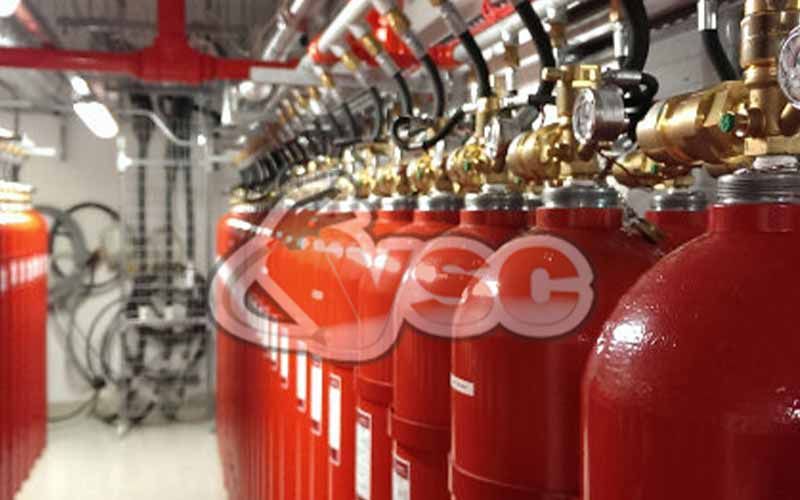
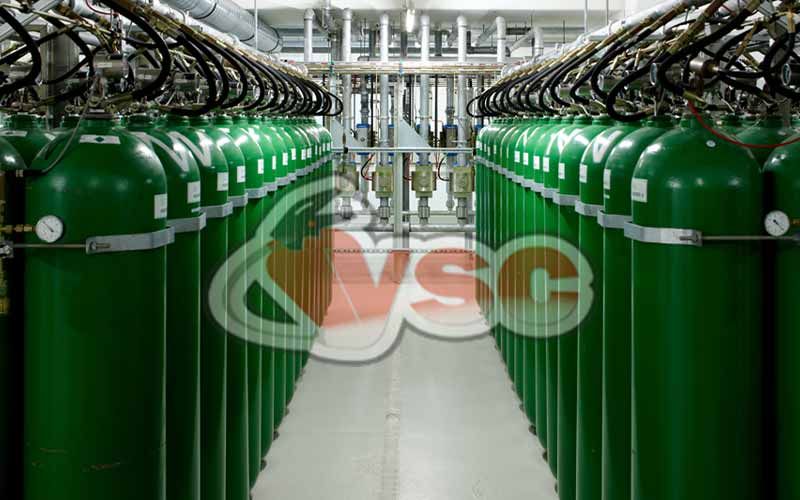
- Available in 80 & 140-liter cylinders for storage.
- Discharge time: 60 seconds.
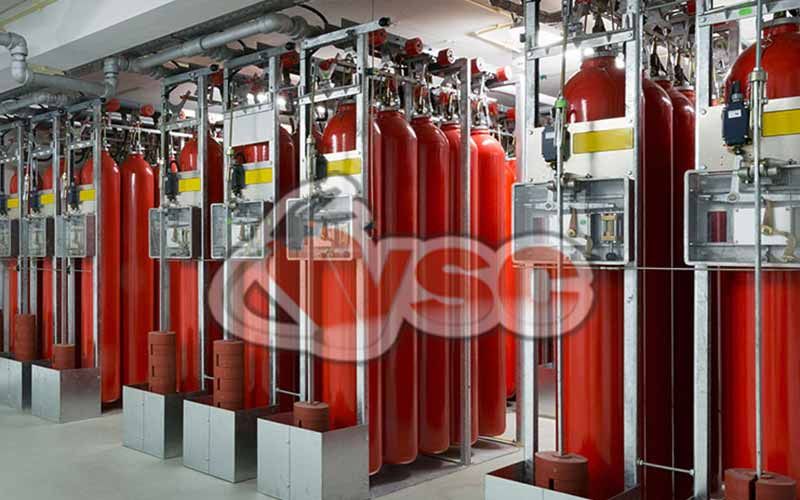
- Can be used with single or multiple cylinders.
- Multiple spaces can be protected from the same center using directional valves.
- Non-mixed gas (compared to IG-55 and IG541 systems, it has lower refilling costs and ease of refilling).
- Easily available and refillable locally.
Argon gas fire suppression systems reduce the oxygen level in the environment between 10.5% to 13.5%, inhibiting the circulation of air that feeds the fire and effectively suffocating it. The extinguishing gas inside the cylinders is pressurized at 200 or 300 bars. The primary purpose of this fire suppression system, developed as an alternative to Halon gas, is to extinguish fires without harming human health. It accomplishes this objective with a 100% success rate in all fire incidents where it is used.
Argon Gas Extinguishing
Indeed, since argon gas is naturally occurring in the environment, it does not cause any harm to nature. Being a non-chemical gas, it is not considered among the recyclable gases. Due to these properties, argon gas fire suppression systems are widely used, and they serve as a preventative measure against various fire disasters. These systems play a crucial role in protecting against fire incidents while also being environmentally friendly, as they do not contribute to ozone depletion or have any adverse effects on the ecosystem.
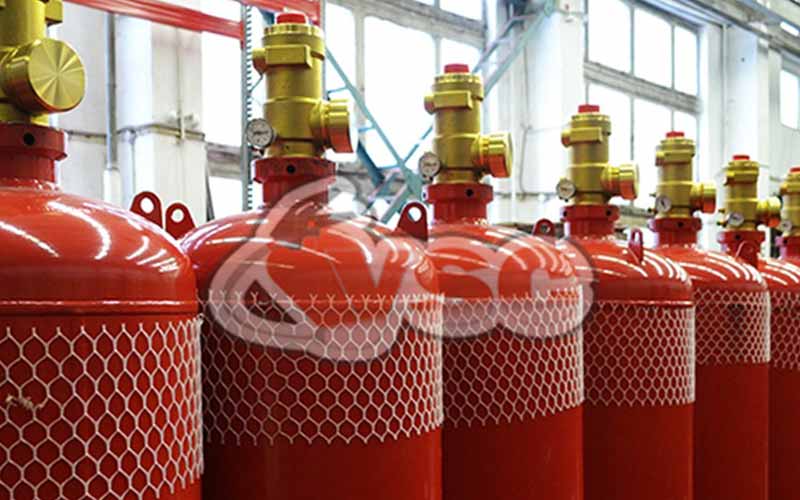

Argon Gas Extinguishing Systems Fire
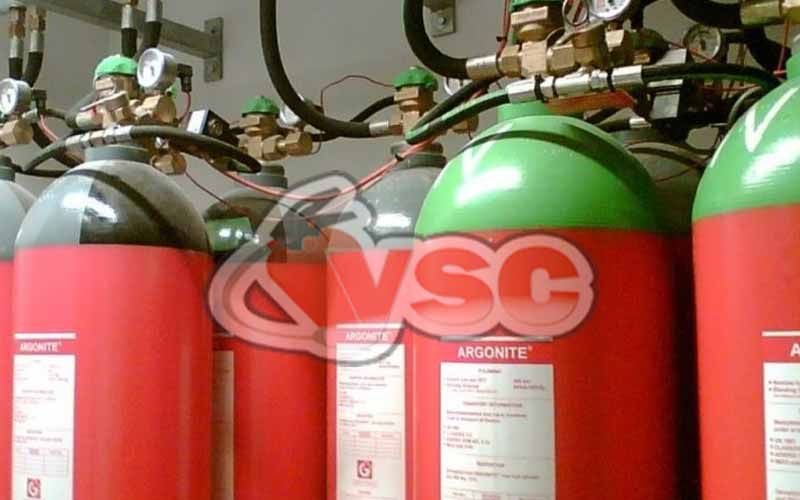
Argon gas fire suppression systems are widely used in fire-prone areas and play a crucial role in preventing major disasters. These systems contain four different gases, including natural gases found in the environment. Argon, argonite, nitrogen, and inergen gases are chemically composed to form this fire suppression mixture. These gases are colorless, odorless, and non-conductive. They have no impact on global warming and do not harm the ozone layer.
During a fire incident, these systems reduce the oxygen level in the area, leaving no residue, and requiring no additional cleanup. The gas discharges within 60 seconds, effectively suffocating and extinguishing the fire. After being used, argon gas fire suppression systems can be easily refilled, making them a convenient fire suppression method.
Argon gas fire suppression systems are commonly used in various areas, including airports, metro stations, chemical storage facilities, high-quality chemical laboratories, transformer stations, marinas, gas industry facilities, petrochemical industrial plants, libraries, archives, museums, electrical rooms, specialized rooms with electronic equipment, system and server rooms, data centers, and energy production facilities.
-
FM-200 Gas Fire Suppression Systems
-
Kitchen Hood Fire Suppression Systems
-
Sprinkler Fire Suppression Systems
-
Carbon Dioxide Extinguishing Systems, CO2 (What is it? How is it used?)
-
FE25 Gas Extinguishing Systems (Working Principle and Price)
-
In-Panel Micro Extinguishing Systems (Electricity Panel)
-
Clean Gas Fire Suppression Systems (How Does It Work? Gases Used?)
-
NOVEC 1230 Fire Suppression Systems (Gas)
-
Argon Gas Extinguishing Systems (INERT Gas, Turnkey)
-
Vehicle Extinguishing Systems (Tube, Maintenance)
-
Fire Detection and Warning Systems
-
Foam Extinguishing Systems